BEE important questions and answers
Here are few important questions with answers.
Do check it out.
1. A 3 φ 4 pole 50 hz induction motor runs at 1460 r.p.m. find its % of slip.
Solution
N s = 120f/p
= 120*50/4
= 1500r.p.m. Running speed of motor
n= 1460r.p.m. Slip S=( N s–N)/ N s*100
=(1500-1460) x 100 / 1500
= 2.667%
2. Explain the working principle of Transformer.
A Transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another by electromagnetic induction (transformer action). The electrical energy is always transferred without a change in frequency, but may involve changes in magnitudes of voltage and current. Because a transformer works on the principle of electromagnetic induction, it must be used with an input source voltage that varies in amplitude. There are many types of power that fit this description; for ease of explanation and understanding, transformer action will be explained using an ac voltage as the input source.
The amount of power used by the load of an electrical circuit is equal to the current in the load times the voltage across the load, or P = EI. If, for example, the load in anelectrical circuit requires an input of 2 amperes at 10 volts (20 watts) and the source is capable of delivering only 1 ampere at 20 volts, the circuit could not normally be used with this particular source. However, if a transformer is connected between the source and the load, the voltage can be decreased (stepped down) to 10 volts and the current increased (stepped up) to 2 amperes. Notice in the above case that the power remains the same. That is, 20 volts times 1 ampere equals the same power as 10 volts times 2 amperes.
A Transformer consists of the following parts
• A primary coil or winding.
• A secondary coil or winding.
• A core that supports the coils or windings.
The primary winding is connected to a 50 hertz ac voltage source. The magnetic field (flux) builds up (expands) and collapses (contracts) about the primary winding. The expanding and contracting magnetic field around the primary winding cuts the secondary winding and induces an alternating voltage into the winding. This voltage causes alternating current to flow through the load. The voltage may be stepped up or down depending on the design of the primary and secondary windings.
3. Calculate the amount of resistance (R) in a circuit, given values of voltage (E) and current (I):
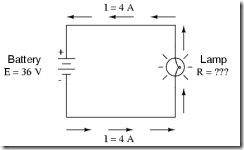
the amount of resistance (R) offered by the lamp
4. calculate the amount of voltage supplied by a battery, given values of
current (I) and resistance (R):

the amount of voltage provided by the battery
5. Calculate the electric power in the given circuit and discuss the effect ofincreasing the battery voltage.
The formula for determining the power in an electric circuit: by multiplying the voltage in "volts" by the current in "amps" we arrive at an answer in "watts." Let's apply this to the given circuit.

In the above circuit, we know we have a battery voltage of 18 volts and a
lamp resistance of 3 Ω.
Using Ohm's Law to determine current, we get:

Now that we know the current, we can take that value and multiply it by
the voltage to determine power:
6. What is meant by DEFLECTING TORQUE ?
The deflecting torque is produced by making use of one of the magnetic, chemical, electrostatic and electromagnetic induction effects of current or voltage and causes the moving system of the instrument to move from its zero position when the instrument is connected in an electrical circuit to measure the electrical quantity. The method of producing this torque depend upon the type of instrument. In attracting the type of instrument, this torque to equal to
Td = 1/2 I2 dL/dθ
Whereas in Pmmc instruments
Td = Bilur
Where B - magnetic density
i - current flowing l - length of coil
u - number of turn r - radius of coil
7. Find the voltage across each resistors in the following circuit.


8. The effective resistance of two resistors connected in series is 100
When connected in parallel, then effective value in 24 ohm’s. Determine the value of two resistors
Series R1+R2=100
R1R2/R1+R2 = 24
R1R2/100 = 24
R1R2 =2400
R1 (100-R1) = 2400
100 R1-R1^2-2400 = 0
R1^2-100 R1 + 2400 = 0 (R1-60)(R1-40) = 0
There Fore R1 = 60; R1 = 40
When R1 = 60

When R1 = 40
9. Find the Req between two points A & B.
1/Req = ½+1/3+1/3 = 1.17 (Req = 1/1.17= 0.8547)
1/Req = 2+.85+4
Req = 7.2
10. Explain about Krichoffs voltage and current laws.
Kirchhoff’s Current Law
The sum of current flowing towards a function is equal to the current
flowing away from it.

Consider a function formed by 6 conductors. The current in these conductors are i1, i2, .i6.Some of these currents are flowing towards a 8 other’s away from A
According to Kirchhoff’s Law, i1+i4+i5+i6 = i2+i3
(Flowing towards) (Flowing away from A)
Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (II Law)
In a closed circuit, the sum of the potential drops is equal to the sum of the potential resistance
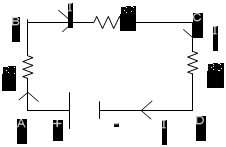
ABCDA forms a closed circuit.
From A -> B, We have a potential drop of IR1. From D -> A, We have a potential drop of V. Sum of potential drops = IR1+IR2+IR3
Potential rise from D -> A =V IR1+IR2+IR3 = V














BEE important questions with answers in the form of pdf
ReplyDeleteSuper 😗
ReplyDelete